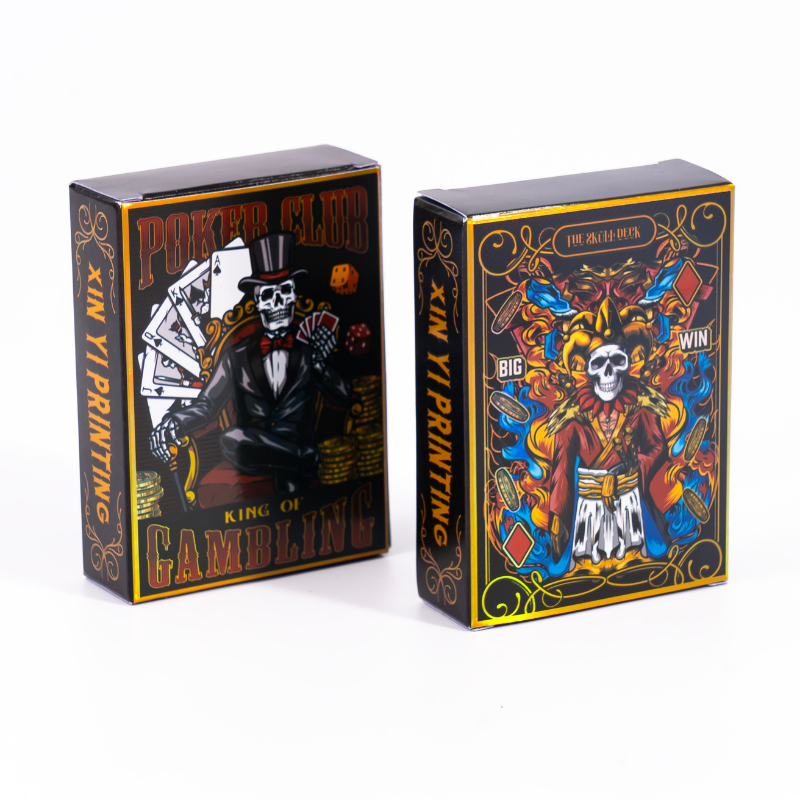
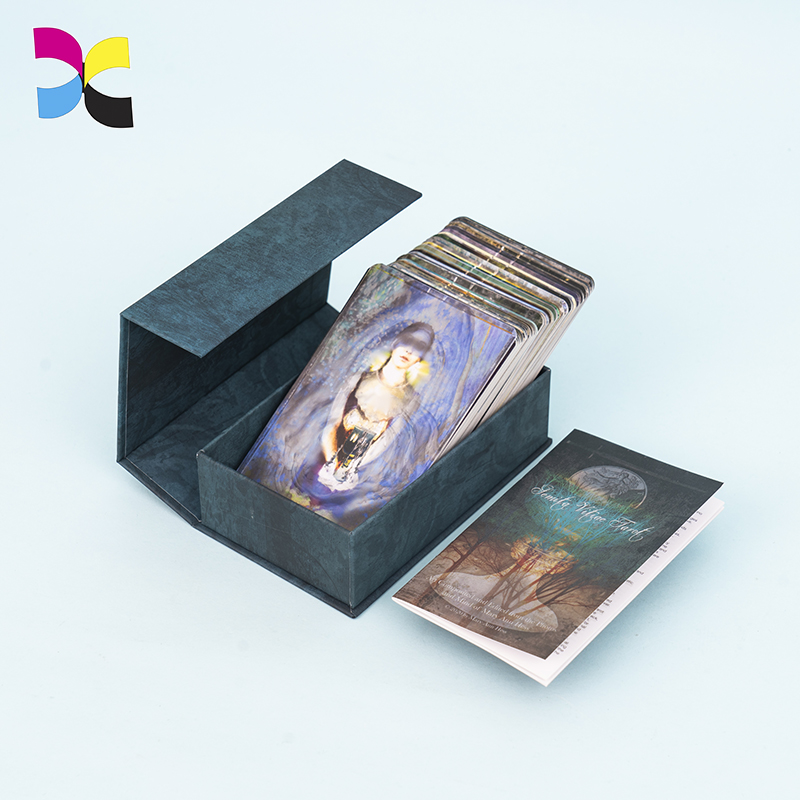
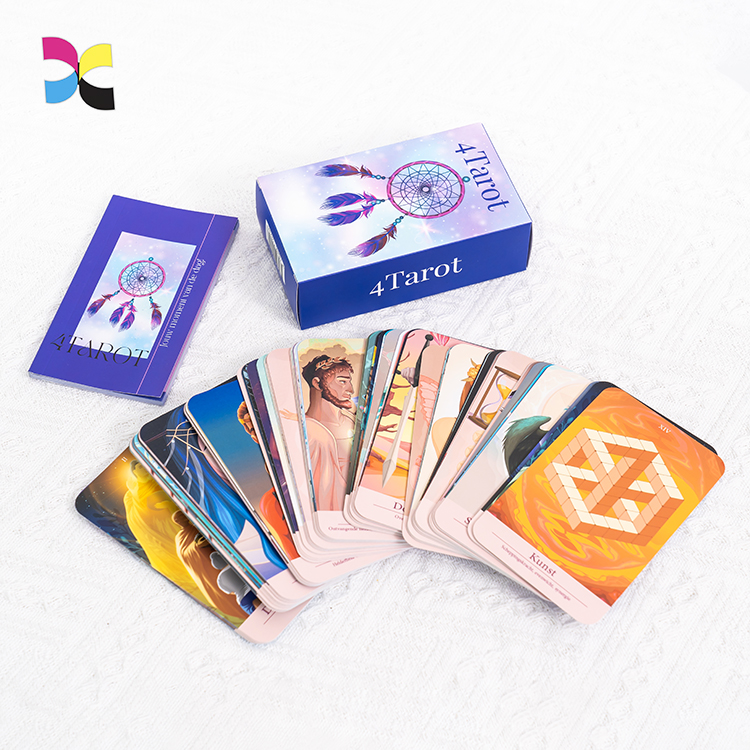
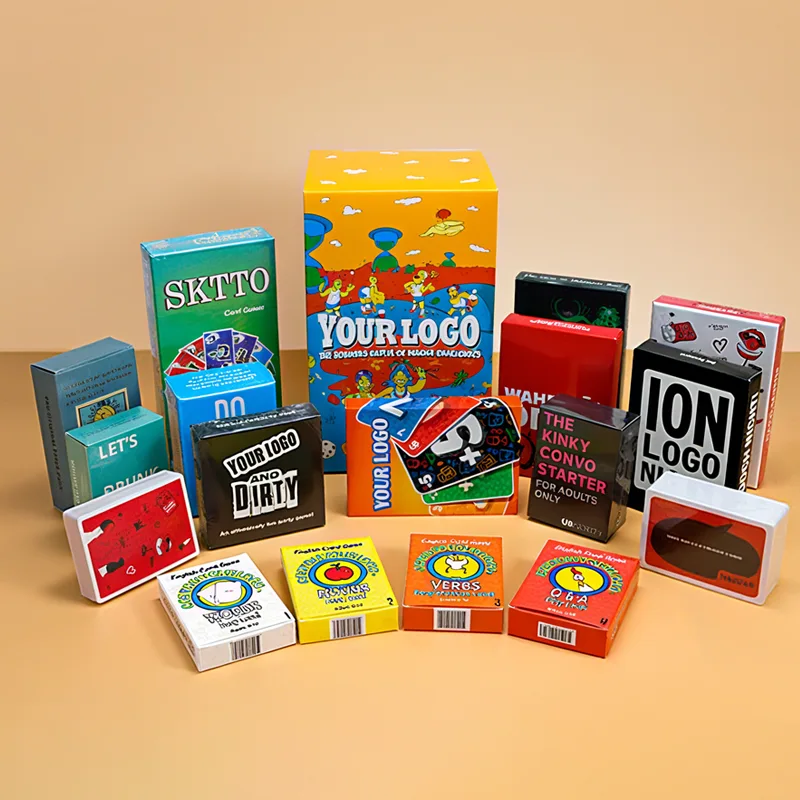
Holographic cards are widely used in trading cards, collectible games, promotional cards, and premium brand packaging. Their shimmering surface and light-reactive effects instantly elevate perceived value and shelf appeal.
However, printing holographic cards at a professional level is very different from home experiments or small-batch DIY methods. In commercial card production, holographic effects must be stable, repeatable, and compatible with mass printing, cutting, and finishing processes.
As a professional card printing manufacturer with decades of experience in custom card production, Xinyi Printing works with global brands, publishers, and game creators to produce high-quality holographic cards at scale. This guide explains how holographic cards are printed in industrial production, what materials and technologies are involved, and what brands should consider when planning holographic card projects.
What Are Holographic Cards in Professional Printing?
In professional printing, holographic cards are printed cards that use holographic foil, film, or pre‑holographic board to create iridescent, rainbow, or depth effects across all or part of the card surface. Unlike simple metallic or foil cards, holographic cards rely on micro‑embossed diffraction patterns in the film that split light into multiple colors as the viewing angle changes.
For brands, game publishers, and artists, holographic card printing is specifically used to:
- Trading cards and collectible cards, such as sports cards, anime cards, and TCG/CCG releases, where holographic effects are used for rare, special, or limited-edition cards.
- Tarot cards and oracle cards, often using full holographic backs or spot holographic elements to enhance visual depth and thematic atmosphere.
- Game cards and board game components, including character cards, ability cards, and expansion cards that require higher visual impact.
- Membership cards and VIP cards, where holographic finishes convey exclusivity and premium positioning.
- Gift cards and prepaid cards, designed to stand out in retail environments and promotional displays.
- Promotional cards and brand cards, used for marketing campaigns, product launches, and event giveaways.
- Art cards and limited artist editions, where holographic elements are applied selectively to highlight artwork or special releases.
- Authentication, warranty, or certificate cards, where holographic surfaces support visual security and authenticity recognition.
Common Types of Holographic Effects Used in Card Printing

Professional holographic card printing offers multiple effect types; choosing the right one is a key creative and technical decision. Common options include:
- Full‑bleed holographic background
The entire card is printed on holographic card stock or laminated film, and your artwork sits on top, allowing the pattern to shimmer through midtones and light areas. This is popular for holo trading cards and collectible game cards. - Spot or selective holographic foil
A holographic foil is applied only to specific design elements—logos, titles, borders, rarity stamps, or special symbols—using hot foil, cold foil, or digital foil techniques. This creates a controlled “spot holo” effect that emphasizes brand or gameplay elements. - Patterned holographic textures
Professional suppliers offer numerous diffraction patterns: rainbow, shattered glass, starlight, honeycomb, wave, pixel, etc. These patterns can dramatically change how the light plays across the card and should be selected to match the style of your artwork and target audience.
Materials Used for Printing Holographic Cards
Choosing the right material combination is critical for both print quality and durability—especially for decks that will be shuffled and handled frequently. Xinyi Printing typically considers the following layers and components:
Base card stock
Common choices for holographic trading cards and game cards include 300–400 gsm coated art board, specialty game card stock with a black or blue core, and FSC‑certified or recycled boards for sustainable projects.
If you are not familiar with different measurement units for card size and paper weight when working with international printers, you can refer to our paper weight conversion guide for a clear breakdown.
Holographic substrate
- Pre‑holographic card stock (foil laminated to board at the mill or converter).
- Holographic film (PET or similar) laminated to printed sheets or to raw board, depending on the process.
- Holographic foil rolls for hot foil stamping, cold foil, or digital foil.
Surface finishes and protection

To control gloss and add protection, manufacturers use gloss or matte lamination, soft‑touch laminate, or UV varnish over the printed areas, sometimes in combination with holographic effects. This improves scratch resistance and card stiffness while keeping the “holo” look crisp over time.
How Holographic Cards Are Printed in Industrial Production
In industrial holographic card production, the process is engineered for color consistency, registration accuracy, and high yield—not just visual impact. A typical manufacturing workflow at a professional card printer like Xinyi Printing includes:
1. Prepress and file preparation
- Checking size, bleed, safe area, and resolution for standard trading card sizes (e.g., 63 × 88 mm) or custom formats.
- Separating artwork into CMYK print layers and dedicated holographic/foil layers using vector masks or spot colors.
2. Printing on holographic stock or base board
- For full‑bleed holographic cards, CMYK artwork is printed directly onto holographic card stock or laminated film using offset or high‑end digital presses.
- For spot holo, the base design is printed first onto premium board and then receives foil in a second step.
3. Applying holographic effect

- Hot foil stamping: A metal die and heated press transfer holographic foil to specific areas under pressure, ideal for sharp, metallic details.
- Cold foil: UV‑curable adhesive is printed where the foil should stick, and holographic foil is transferred inline on the press—excellent for fine halftones and gradients.
- Digital foil: Toner or varnish is digitally printed as a mask, then the sheet is passed through a foiling unit—suited to short runs and variable designs.
4. Lamination and coating
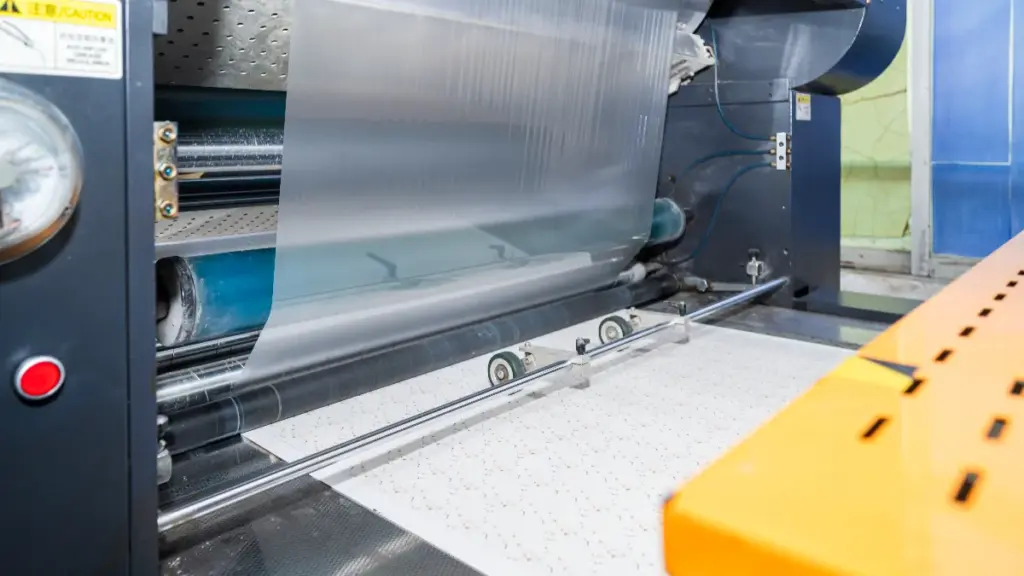

Where needed, an additional laminate or varnish is added to protect the printed and foiled surface, improve handling, and control gloss or tactile feel.
5. Die‑cutting, corner rounding, and collation
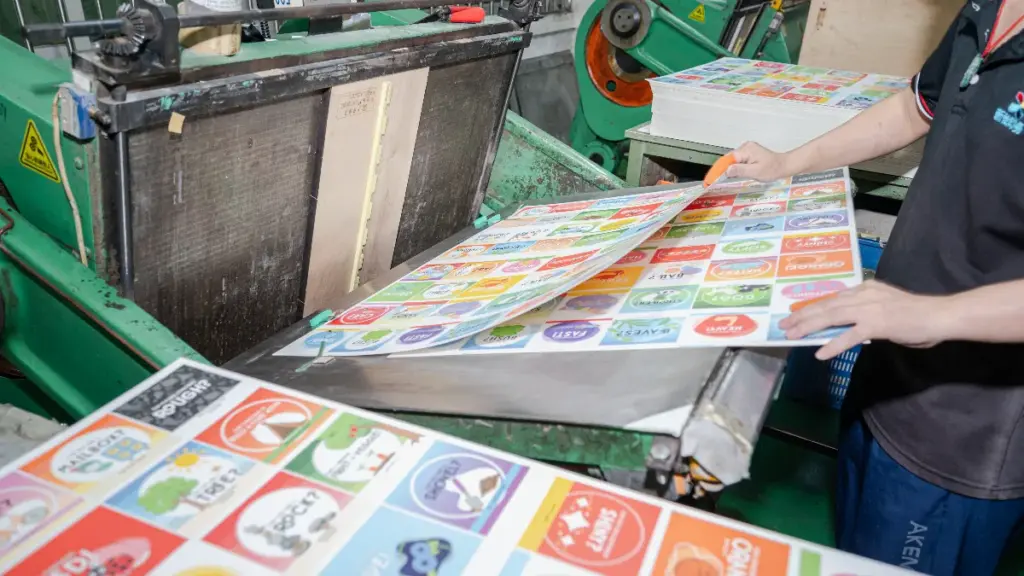

Cards are cut to final size using high‑precision guillotines or steel rule dies, corners can be rounded, and decks are collated, shrink‑wrapped, or packed into custom boxes or tuck cases.
Printing Technologies Used for Holographic Cards
Different holographic card projects call for different printing technologies, depending on run size, color requirements, and foil complexity. Common printing technologies include:
UV Offset Lithographic Printing (UV Offset)

UV offset is one of the most common methods for printing on holographic paper and foil‑laminated board because the substrate does not absorb conventional inks well. UV‑curable inks are transferred via offset plates and then cured instantly with ultraviolet light, giving:
- Vivid color and sharp details on non‑porous holographic surfaces.
- Excellent adhesion on laminated or metallic boards used for full‑bleed holographic cards.
Conventional Offset Lithographic Printing
Conventional offset uses heat and air to dry the ink and is well‑suited to standard coated card stocks without lamination. For holographic projects, it is mainly used when:
- The holographic effect is added later via cold foil or hot foil stamping on a non‑laminated board.
- The card does not use pre‑holographic stock but relies on foil embellishment instead.
Digital Printing (Toner and Inkjet Systems)
High‑end digital presses are widely used for short runs, prototypes, and on‑demand holographic card printing. Digital printing can be combined with:
- Digital foil / digital embellishment units for spot holographic foil and raised foil details on small batches.
- White toner or white ink layers to control where the holographic background is blocked or allowed to shine through.
Hot Foil Stamping (Holographic Foil
Hot foil stamping uses a metal or polymer die, heat, and pressure to transfer holographic foil onto specific areas of an already printed card. It is the classic choice for:
- Spot holographic logos, titles, borders, and rarity icons.
- Creating raised or debossed holographic effects with strong metallic impact.
Cold Foil Transfer (Inline Foiling)
In cold foil, a UV‑curable adhesive image is printed on the sheet, then holographic foil is transferred inline on the press and overprinted with CMYK. This method is ideal for:
- Full‑color images printed over holographic foil, with precise registration.
- Complex gradients and fine halftones that are difficult to achieve with traditional hot foil stamping.
Screen Printing and UV Screen Varnish
Screen printing is sometimes used on holographic cards to add thick UV varnish, spot textures, or extra‑opaque white layers on top of holographic substrates. It is especially useful when:
- You want raised, tactile effects over holographic areas.
- You need strong blocking white underprint on very intense holographic patterns.
Here is a summarized table about common printing technologies in holographic cards printing:
| Printing method | Main use on holographic cards | Typical run size | Key advantages | Typical limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV offset lithographic printing | CMYK printing on holographic paper or foil‑laminated board | Medium–large | Excellent color, sharp detail, fast curing on non‑porous holo substrates | Higher setup cost, less flexible for frequent design changes |
| Conventional offset printing | Base CMYK print on standard board before foil or laminate | Medium–large | Very consistent color, economical at scale | Not ideal directly on holographic film; slower drying vs UV |
| Digital printing (toner / inkjet) | Short‑run holographic cards, prototypes, POD with optional digital foil | Small runs | Low setup cost, supports variable data and quick changes | Higher unit cost for large volumes; more limited substrates |
| Hot foil stamping | Spot holographic logos, borders, rarity icons | Small–large | Strong metallic impact, crisp edges, classic “stamped” holo look | Requires dies; not ideal for fine gradients or very small text |
| Cold foil transfer | Large holographic areas and CMYK over holographic foil | Medium–large | Inline with printing, great for gradients and detailed images over foil | More complex setup; most efficient at higher volumes |
| Screen printing / UV screen varnish | Thick white, raised UV, textured effects on holo surfaces | Accent use | Very opaque whites, strong tactile finishes | Slower, usually an extra step rather than a main image process |
Design Considerations for Holographic Card Printing
Strong holographic card design is not only about adding “shiny” areas—it’s about planning how color, contrast, and foil interact under real lighting. When Xinyi Printing reviews files, some of the key design considerations include:
- Layering and masks
- Color and readability
- White ink and underprints
When printing on holographic stock, a white ink or underprint layer is often used to control where the holographic background is blocked and where it shines through. This is particularly important for faces, logos, and small typography. - File specifications
Supply print‑ready PDF or vector files in CMYK with sufficient bleed and resolution, and clearly label special colors or foil layers. Clear setup reduces prepress revisions and speeds up proofing
Quality Control in Holographic Card Production
Holographic cards demand stricter quality control than standard cards. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming material checks
Verifying holographic films, foils, and base boards for pattern consistency, thickness, and surface defects before printing starts. - Color and registration control
Using spectrophotometers, press targets, and on‑press monitoring to ensure CMYK colors match approved proofs across the full run. Foil registration is continuously checked so holographic areas align with underlying artwork. - Mechanical and visual inspection
Random sampling of cards for foil coverage, scratch resistance, delamination, warping, and cutting accuracy. For trading card games or professional decks, shuffling feel and card stiffness are also evaluated to ensure a consistent tactile experience.
At Xinyi Printing, holographic card projects undergo material testing, press checks, and post-production inspections to ensure every batch meets export and brand standards.
Common Challenges in Printing Holographic Cards
Below are the most common issues encountered in holographic card printing and how professional manufacturers resolve them.
| Challenge | Root cause | Manufacturing solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poor ink adhesion | Low surface energy of holographic films | UV inks, surface treatment, controlled curing | Durable print with strong scratch resistance |
| Excessive glare | Uncontrolled holographic reflection | Precise white ink blocking in key areas | Clear text and balanced visual contrast |
| Color inconsistency | Color shift on holographic substrates | Material-specific profiling and press calibration | Stable color across batches |
| Layer misregistration | Sheet movement during multi-layer printing | Tight registration control and sheet conditioning | Accurate alignment of all print layers |
| High rejection rate | Minor defects amplified by holographic surfaces | Pre-production trials and in-line QC checks | Reduced waste and consistent output |
| Cost control pressure | Higher material and process cost | Design-for-manufacturing optimization | Controlled cost without quality loss |
Customization Options for Holographic Cards Printing
At Xinyi Printing, typical customization options include:
Sizes and format

Standard trading card size (63 × 88 mm), poker and bridge sizes, mini cards, tarot, oversized promo cards, and fully custom dimensions.
Paper, cores, and finishes
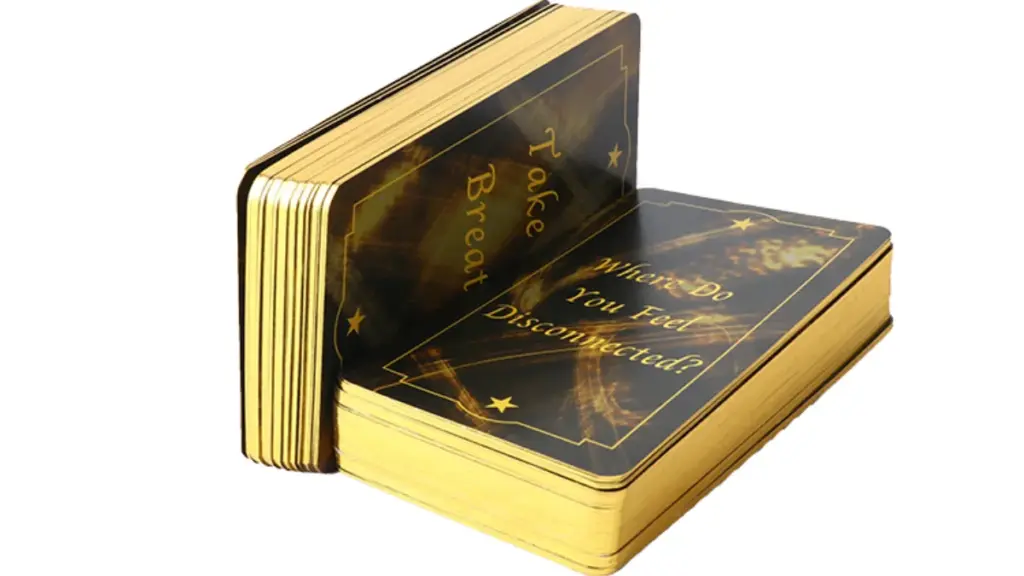

Different card cores (black, blue, or white) for opacity and game feel.
Gloss, matte, soft touch, or textured laminate on top of holographic effects for unique tactile finishes.
Holographic and foil options
Multiple holographic patterns, gold/silver holo foils, colored foils, and combinations of holographic and metallic elements on the same card.
Security and collectibility features
Serial numbering, QR codes, microtext, variable data printing, and anti‑counterfeit holographic elements for limited editions and licensed content.
Packaging and sets
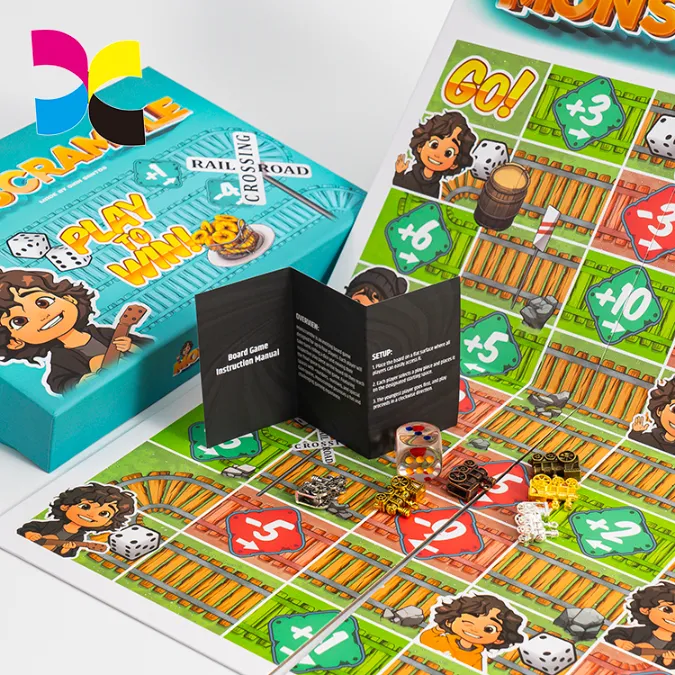


Custom tuck boxes, rigid boxes, booster pack configurations, and retail‑ready packaging designed around your holographic card set.
Why Work With a Professional Holographic Card Manufacturer
While there are many tutorials on how to make holographic cards at home, industrial holographic card printing is a different discipline—one that requires specialized equipment, materials, and process control. Working with a professional holographic card manufacturer like Xinyi Printing gives you several advantages:
- End‑to‑end technical support
From material selection and color management to foil pattern choice and file setup, an experienced team can help you avoid trial‑and‑error and move directly to production‑ready solutions. - Consistent, scalable quality
Industrial presses, automated finishing lines, and formal quality systems ensure that your first 500 cards and your 50,000th card match in color, holo effect, and cut precision. - Compliance, sustainability, and IP protection
A certified manufacturer can provide eco‑friendly materials, meet global safety standards, and protect your artwork and licensed content through NDAs and secure workflows.
If you are planning a new holographic trading card game, a premium deck, or branded holographic card set and want reliable, production‑grade results, partnering with a professional manufacturer like Xinyi Printing is the most efficient way to turn your designs into high‑quality, collectible holographic cards.